
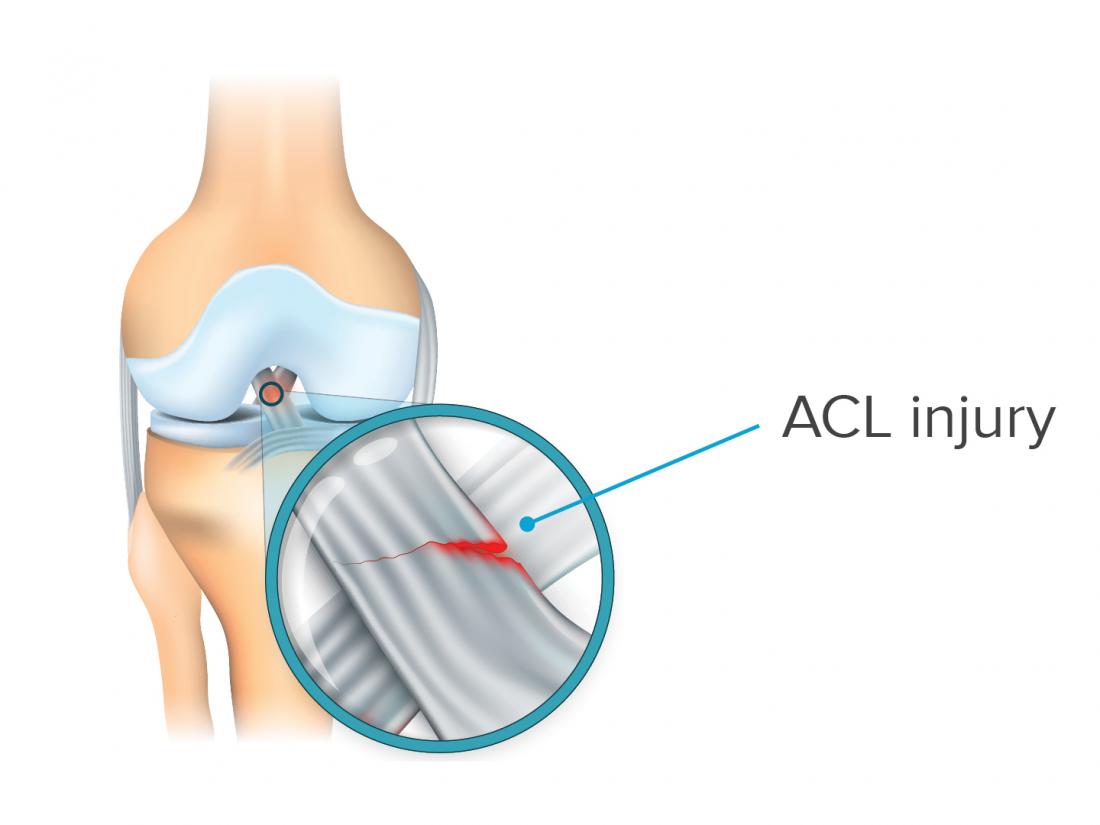
Others may require minimally invasive surgery with an orthopedic surgeon. Some ACL tears can be treated with rest, medication or physical therapy.
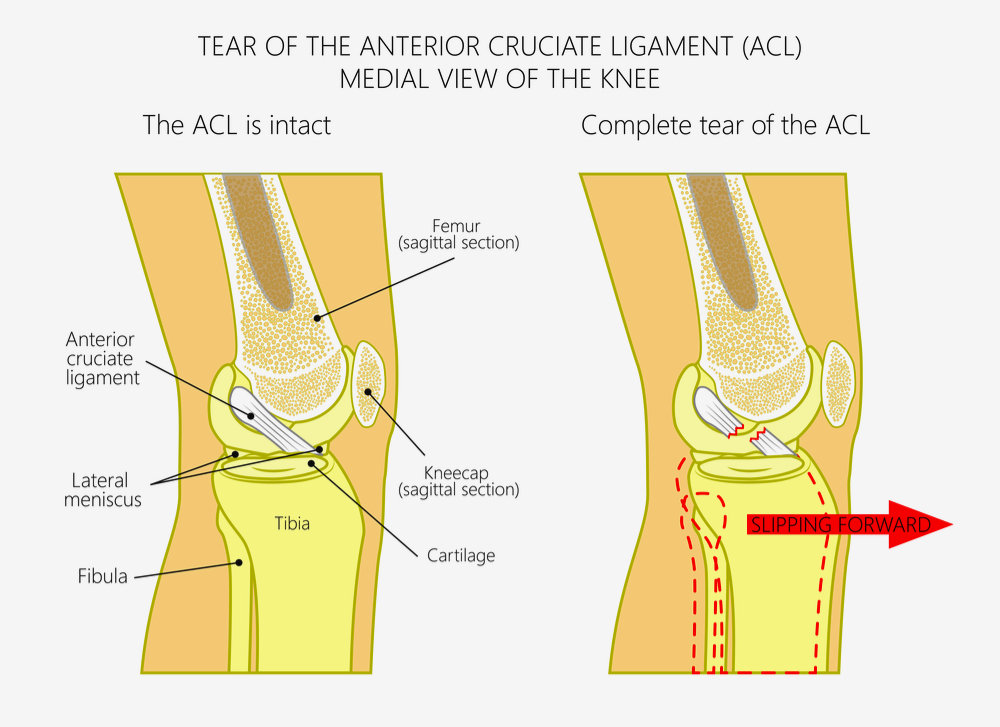
ACL injury typically results from a sudden stopping or twisting motion, often when playing sports.ĪCL treatment varies depending on how severe the injury is. It occurs when the ACL, the key stabilizing ligament behind the kneecap, becomes damaged or torn. Your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments of the knee, connecting your shin and thigh bones behind the kneecap.Īn ACL tear is one of the most common knee injuries. What is an ACL tear?Ī ligament is connective tissue that joins two bones or pieces of cartilage together. Our extensive experience treating ACL tears makes us experts at getting you up and running again. Snapping hip syndrome symptoms & treatment.Piriformis syndrome symptoms & treatment.Though less painful than some procedures, arthroscopy is not pain-free. With a camera probe into the knee, a doctor can look at the anterior cruciate ligament to see how badly torn it is and whether reconstructive surgery is needed. The best way to see a partial tear is arthroscopy. MRIs are not good, however, at providing details about a partial tear. An MRI is nearly 90% accurate in determining whether an anterior cruciate ligament has been torn and how badly. If more tests are needed to determine whether your anterior cruciate ligament is torn, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan will be ordered. If the tibia moves excessively forward, that would strongly suggest a torn anterior cruciate ligament.

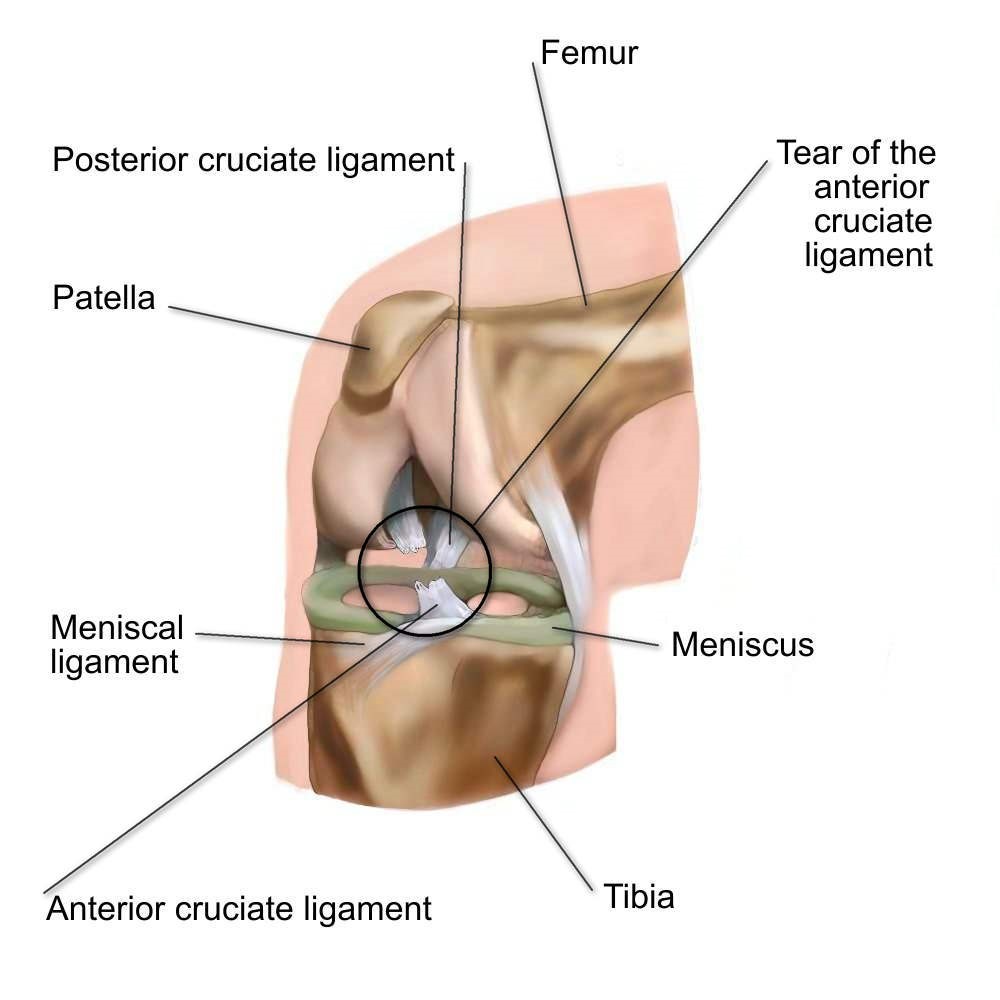
This will help your doctor decide what treatment might be best for you.īecause the anterior cruciate ligament is deep inside the knee, diagnosing the condition can be challenging. You may also be asked about your physical and athletic goals. Your doctor will generally ask you how the injury occurred, whether you've had other knee injuries and how your knee has felt since the injury. Football players have the greatest risk for multiple knee injuries like combined anterior cruciate ligament, medial cruciate ligament and cartilage damage. When a basketball player running down the court plants his foot hard to change direction, his knee buckles as the thighbone and shinbone move in opposite directions, tearing the anterior cruciate ligament.īasketball, soccer and skiing often cause anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Quick changes of direction while running cause most anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Your knee often feels as though it will give way or easily bend backward. Others may feel they can play through the injury. But the movement that causes the ligament to tear often causes damage to other parts of the knee that do have pain receptors. The anterior cruciate ligament itself has no pain receptors. The pain resulting from a torn anterior cruciate ligament varies widely. This happens because the small blood vessels in the ligament also tear and leak blood into the joint. If you tear your anterior cruciate ligament, you may have the sensation of your knee giving out or buckling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
